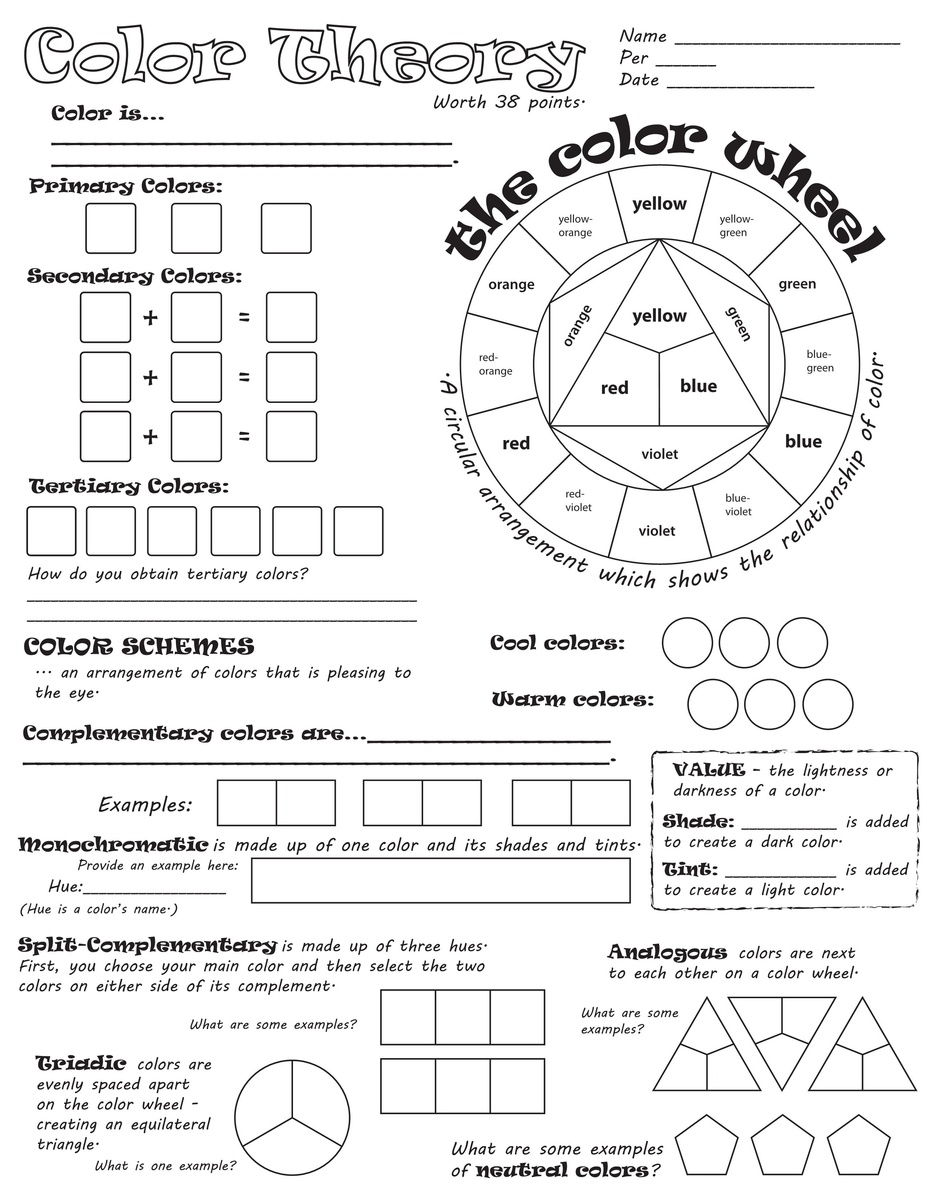
Analogous Colors – Colors closely related in hue; three colors next to each other on the color wheel, such as red, orange, and yellow.
Arbitrary color – Color used creatively by an artist, in which local color is substituted by another color that is usually of a similar value.
Color Temperature – The illusion of warmth or coolness of a color. Red, orange, and yellow appear warm, while blue appears cool. Green and violet are transitional because they can be warm or cool depending on their mixture.
Color Wheel – The spectrum bent into a circle, which is a useful tool for organizing colors. The basic six-color wheel features 3 primary colors next to 3 secondary colors. The twelve-color wheel includes six tertiary colors placed between a primary color and a secondary color.
Complementary Colors – Two colors directly opposite each other on the color wheel. A primary color is complementary to a secondary that is a mixture of the two remaining primaries. The three sets of complementaries are red\green, yellow\violet, and orange\blue.
Hue – A color as it appears in the spectrum or color wheel.
Intensity – The saturation or strength of a color determined by the quality of light reflected from it. A vivid color is of high intensity; a dull color, or low intensity.
Local Color – The naturalistic colorof an object as seen by the eye (green grass, blue sky, red apple, etc.)
Monochrome – Literally “one color”, a color scheme that uses one hue and all the values of that hue.
Neutralized Color – A color that has been grayed or reduced in intensity by mixture with any of the neutrals or with a complementary color.
Primary Color – Unique hues that can’t be created through mixtures of other colors.
Pigment – Color substances, usually powdery in nature, that are used with liquid vehicles to produce paint.
Polychrome – Many colors.
Saturation – The intensity or brightness of a color.
Secondary Color – A mixture of two primaries; green (from yellow and blue), orange (from yellow and red), and violet (from red and blue)
Shade – A dark value of a hue, made by adding black
Simultaneous Contrast – Intensified contrast which results whenever two different colors are placed next to each other.
Spectrum – Separate hues created when a beam of light is refracted by a prism.
Split Complement – A color and either one of two colors on either side of its complement, like orange and violet, or orange and green
Subjective Color – Colors chosen by the artist without regard to the natural appearance of the object portrayed. Subjective colors have nothing to do with objective reality except the expression of the individual artist. Also known as arbitrary color.
Tertiary Color – A mixture of a primary and an adjacent secondary color. For example, a mixture of yellow and orange creates yellow-orange.
Tint – A light value of a hue, made by adding white
Triad – A group of three colors spaced an equal distance apart on the color wheel. The twelve wheel has a primary triad, a secondary triad, and two tertiary triads.